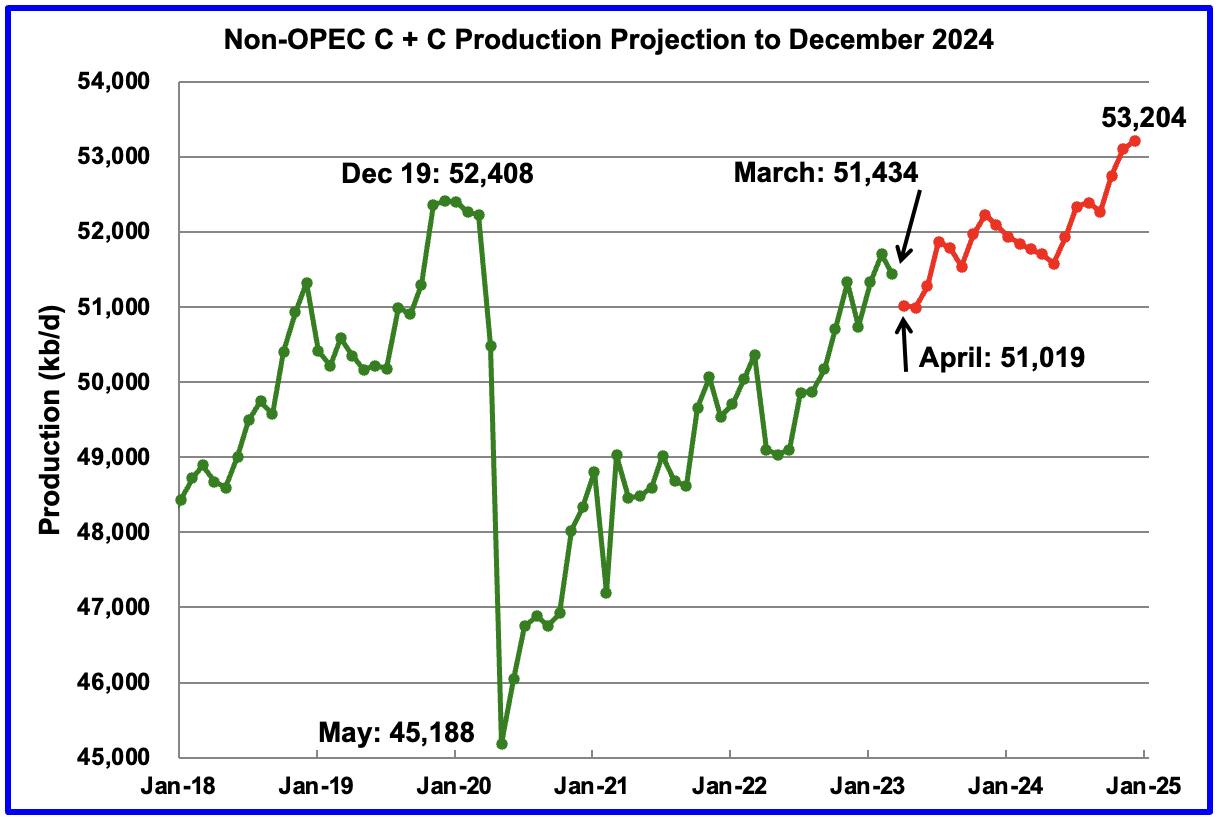
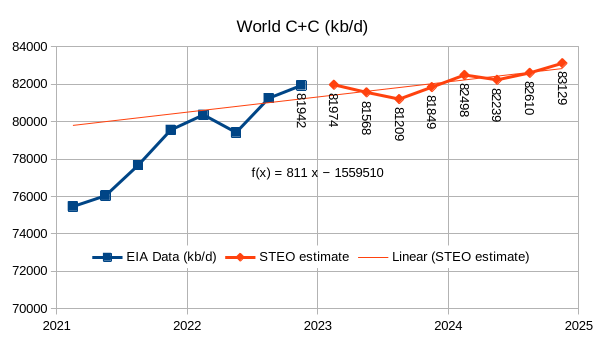
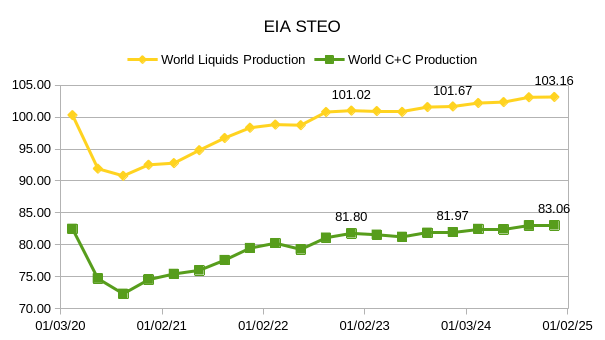
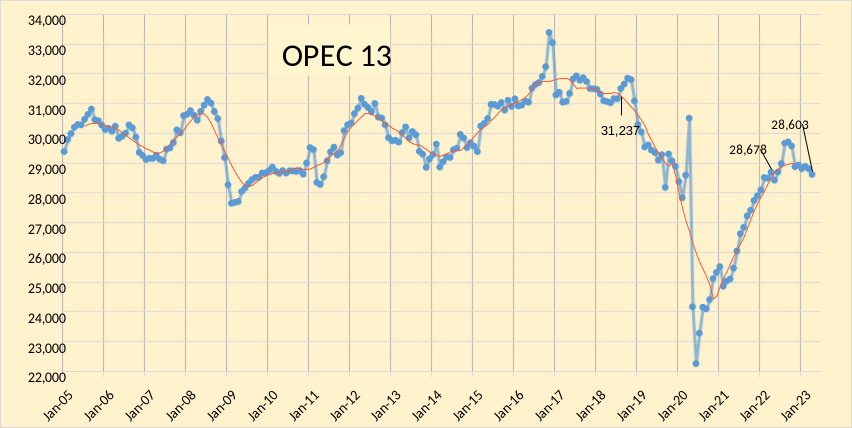
The EIA’s Short Term Energy Outlook (STEO) was published in early July. The chart below estimates World C+C by using the STEO forecast combined with past data from the EIA on World Output.
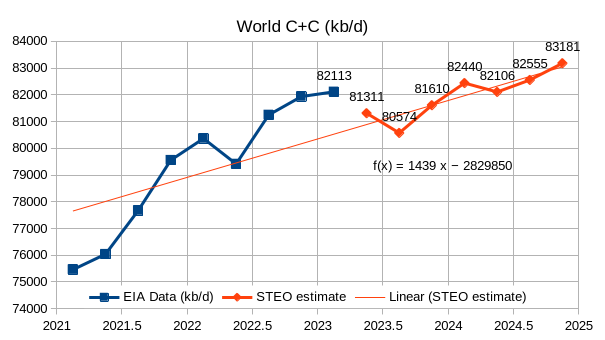
This month we have actual EIA data for 2023Q1 which increases the annual rate of increase for the forecast period compared to last month by 600 kb/d, part of the reason is an 800 kb/d forecasted drop in output from Q1 to Q2 of 2023. If we use the 2023Q1 to 2024Q4 trend the annual rate of increase is 911 kb/d, about a 100 kb/d increase from last month’s estimate. The trend from 2022Q1 to 2024Q4 is similar at about 916 kb/d. If this forecast through 2024Q4 is roughly correct, I expect increases in output after 2024 will be considerably lower, I also think this STEO forecast is optimistic. Annual average output in 2022 was 80.74 Mb/d and increases to 81.4 Mb/d in 2023 and to 82.6 Mb/d in 2024. These annual averages are 0.25 Mb/d less in 2023 and similar for 2024 as last month’s estimates.
Read More