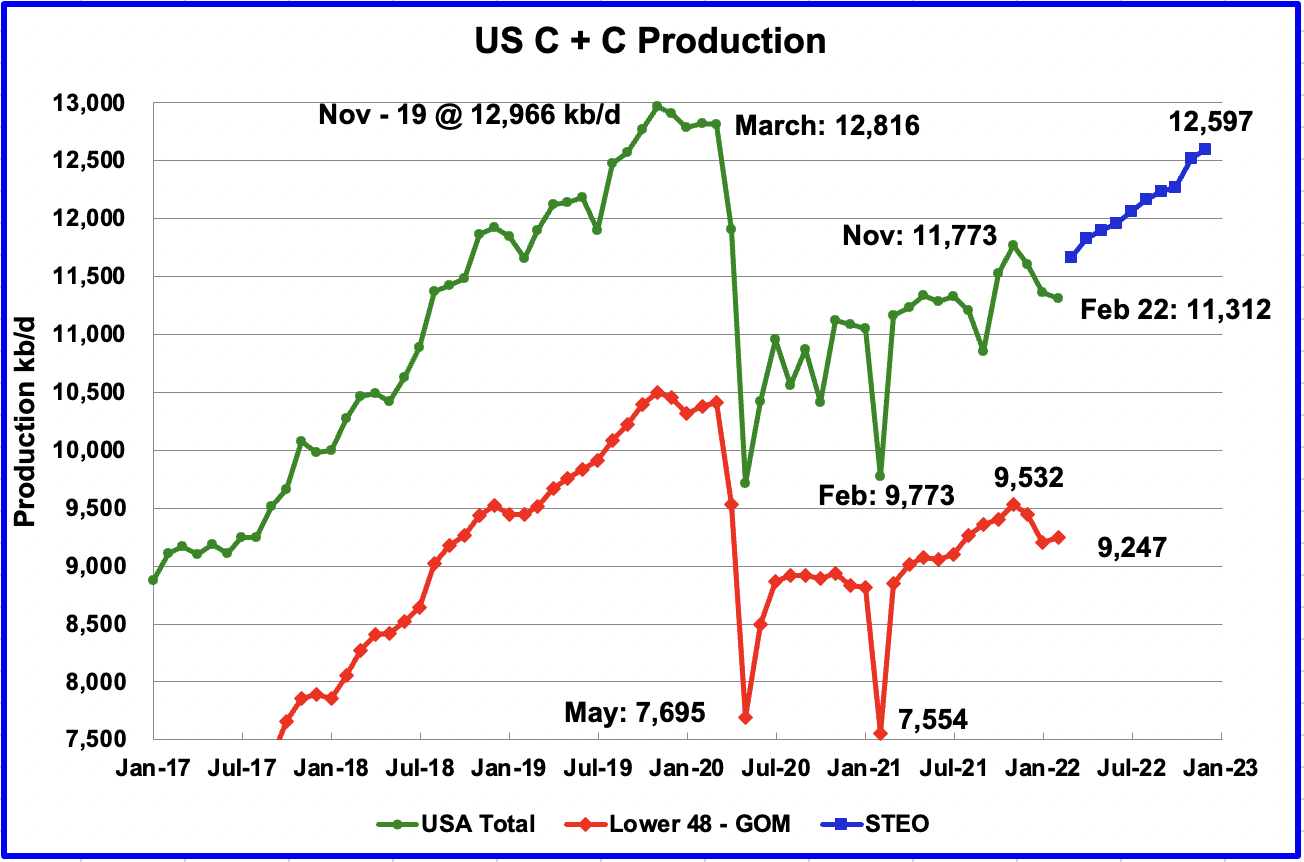
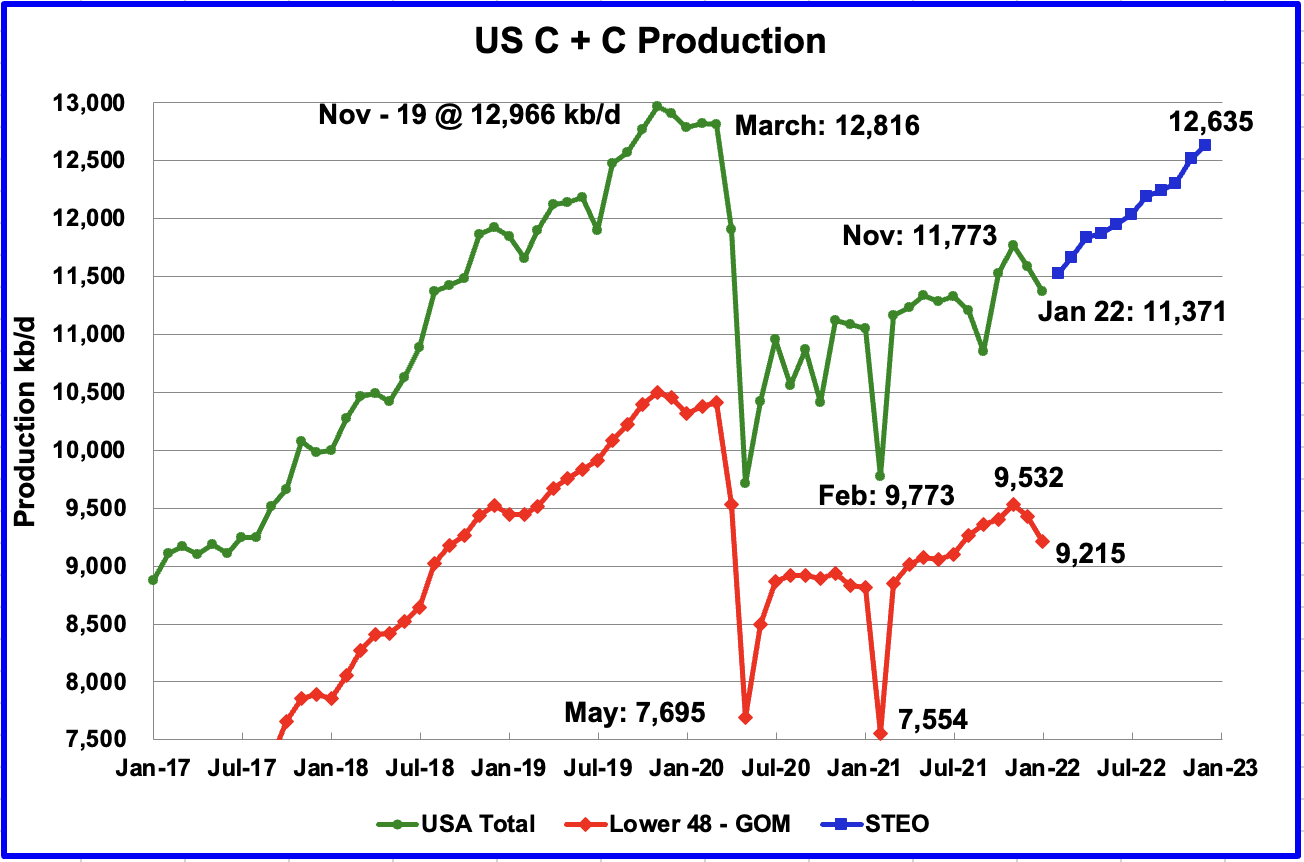
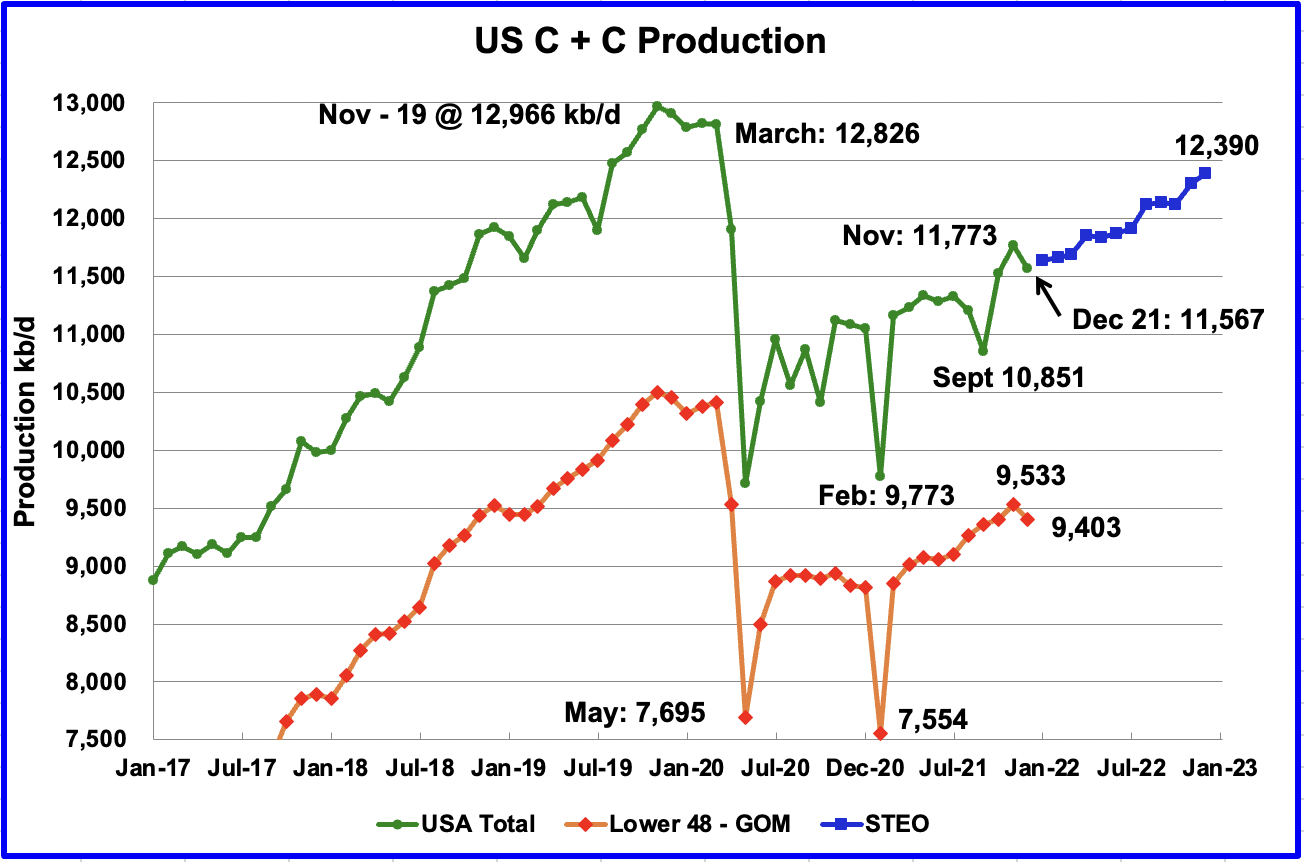
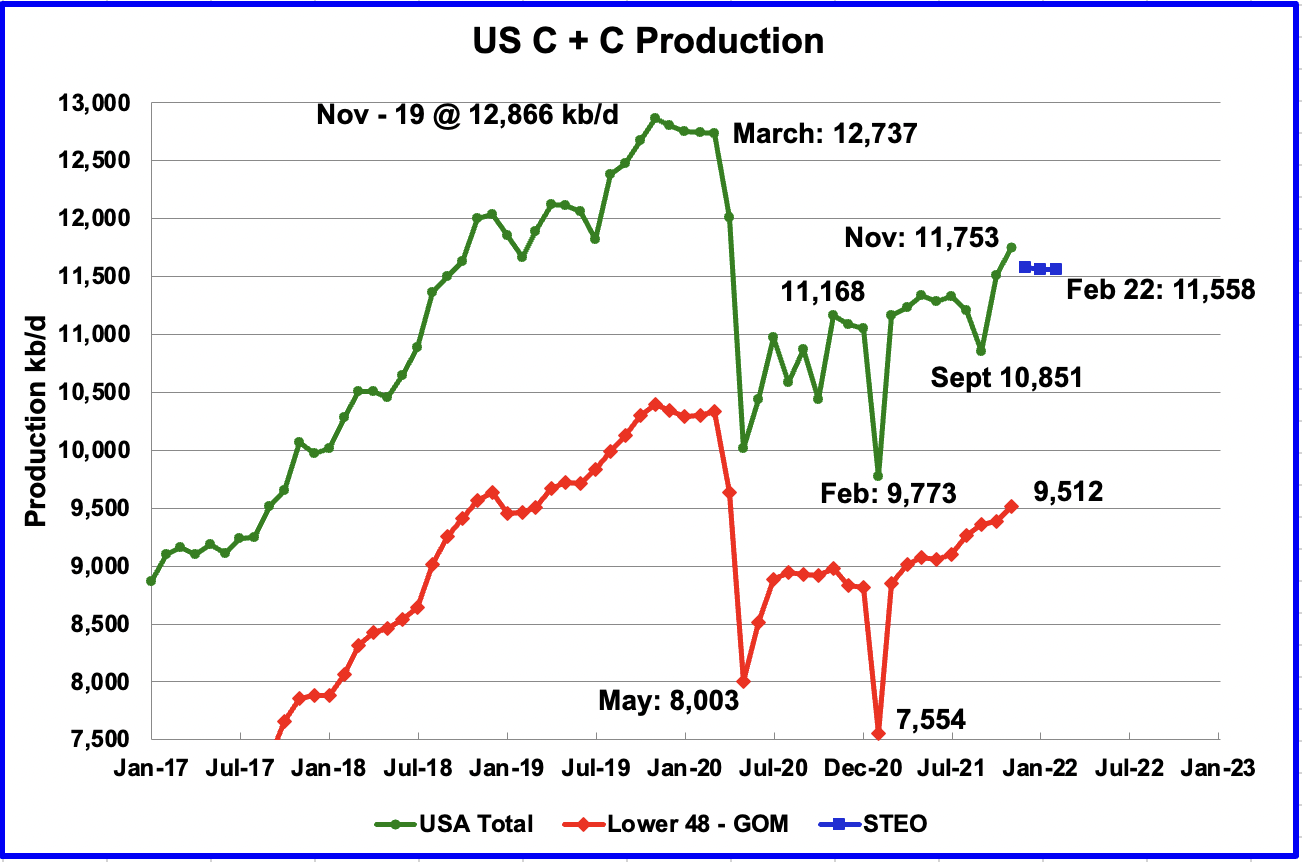
Through 2021 the federal waters of the northern Gulf of Mexico (OCS) have cumulative production of 23.4 Bbo and 193 Tcf. The deepwater (water depths > 1000’ as defined by BOEM) has produced 10.2 Bbo and 23.5 Tcf while the shelf has produced 13.2 Bbo and 169.5 Tcf. From a BOE standpoint, the GOM has primarily been a gas province, and the bulk of that production has come from shelf fields. While the shelf has produced more cumulative oil than deepwater, over 90% of current oil production comes from deepwater fields.
First production from the OCS occurred in 1947. First deepwater production was in 1979 from Shell’s Cognac field in 1022’ of water. GOM oil production in December 2021 was 1.69 mmbopd as per BSEE. As Ovi says in his monthly updates, if GOM were a state, it would be the 2nd leading oil producing state in the US, only behind Texas.
Brief history of GOM gas production
GOM gas production peaked in 1997 at 14.4 bcf/day and has been declining ever since. Current gas production is about 2 bcf/day.
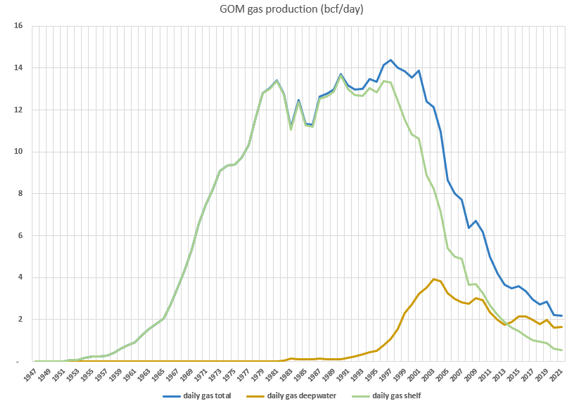
Figure 1 – GOM gas production, with shelf and deepwater broken out. Data from BOEM.
Read More