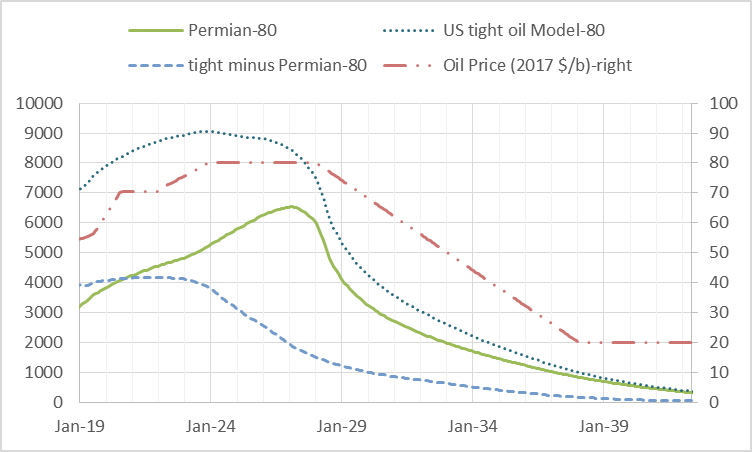
A Guest Post by Islandboy
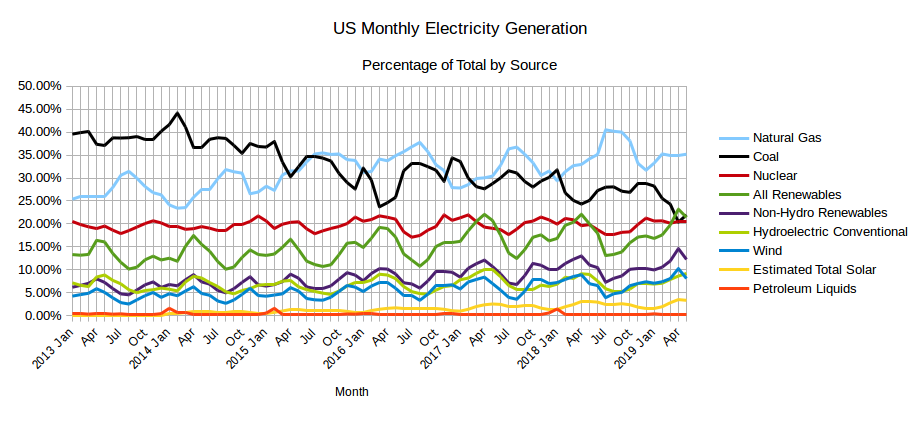
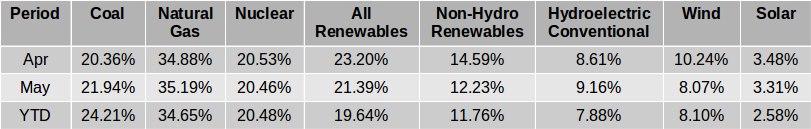
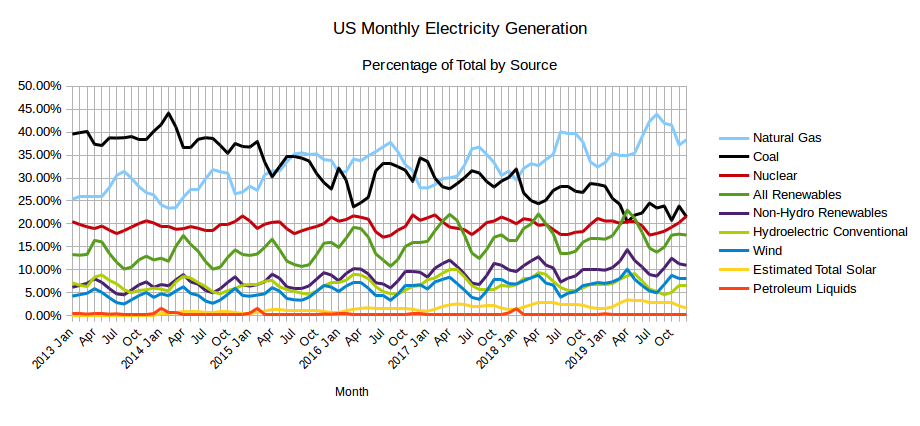
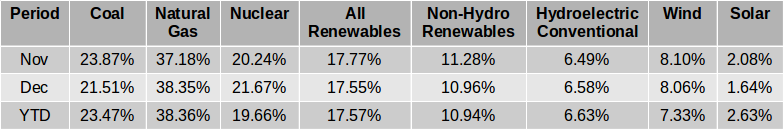
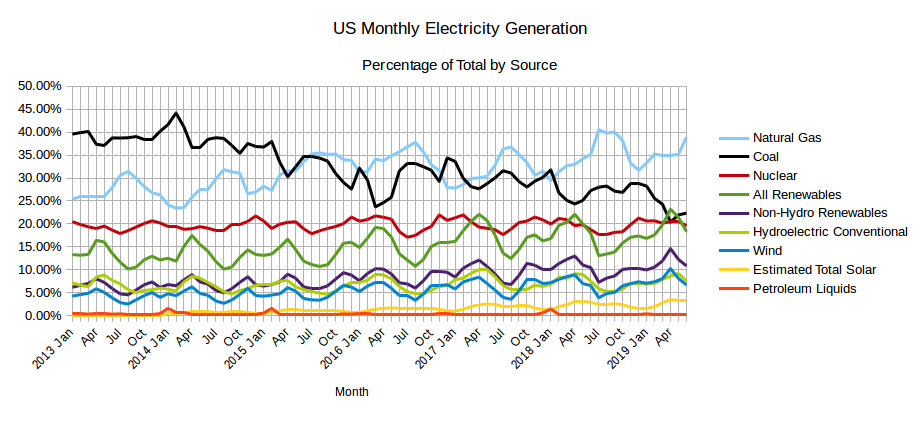
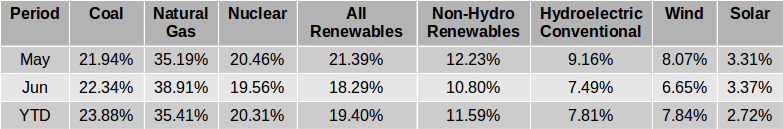
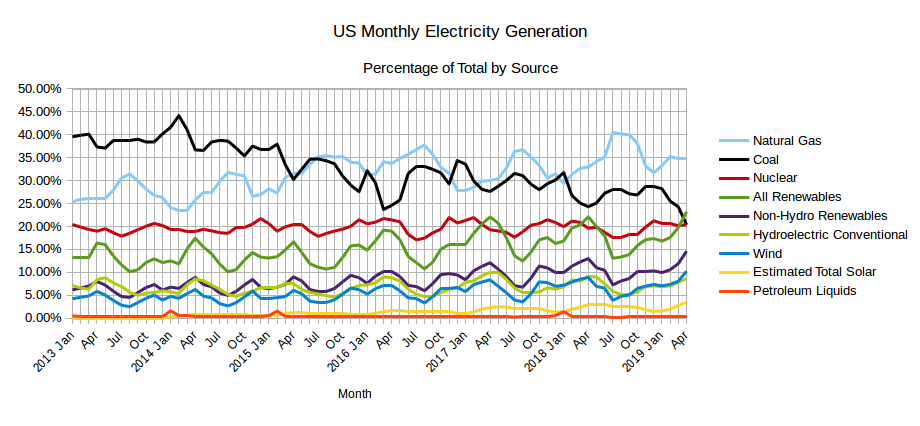
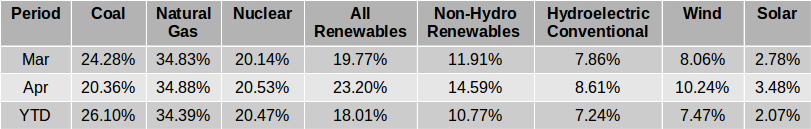
The EIA released the latest edition of their Electric Power Monthly on July 24th, with data for May 2019. The table above shows the percentage contribution of the main fuel sources to two decimal places for the last two months and the year 2019 to date. In April, the EIA in their Short-Term Energy Outlook projected that the contribution from All Renewables would exceed that from Coal for the first time ever in April and possibly in May. While that turned out to be the case in April, in May electricity generation from coal was slightly greater than the amount generated by All Renewables and the EIA expects Coal to generate more than All Renewables each month through to April 2019. Read More