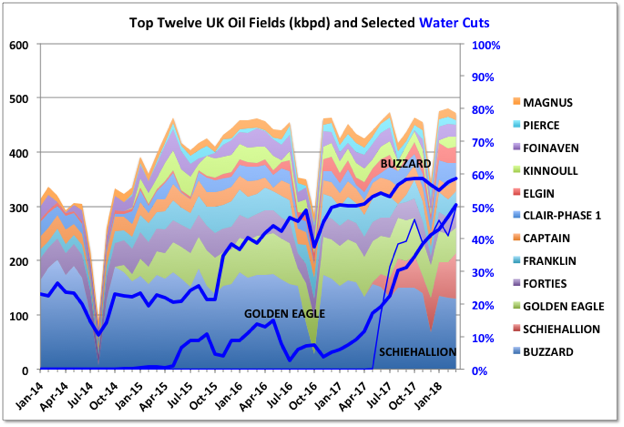
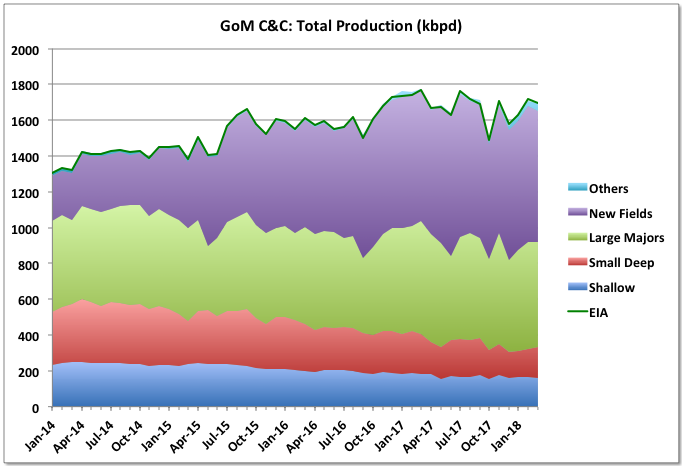
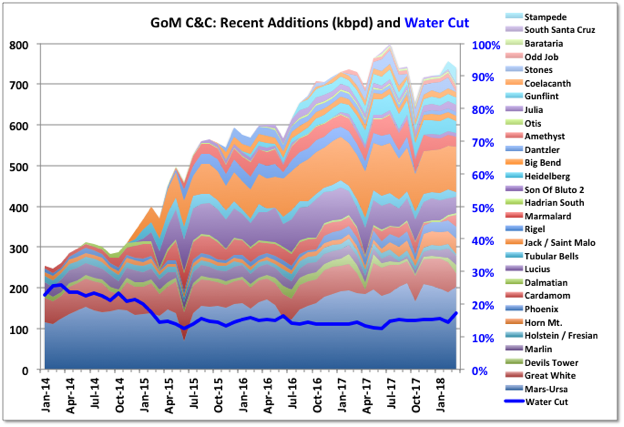
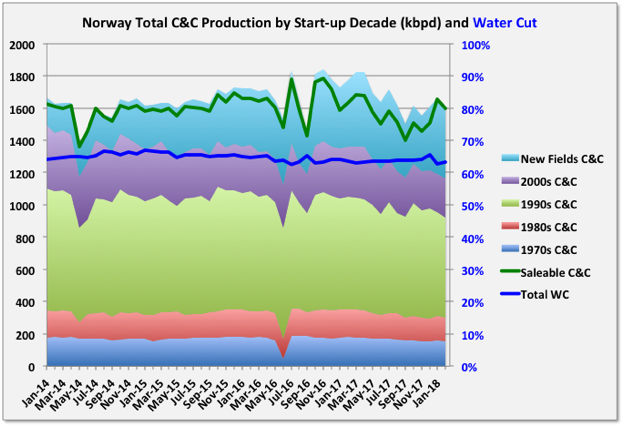
A Guest Post by George Kaplan
Crude and Condensate Reserves
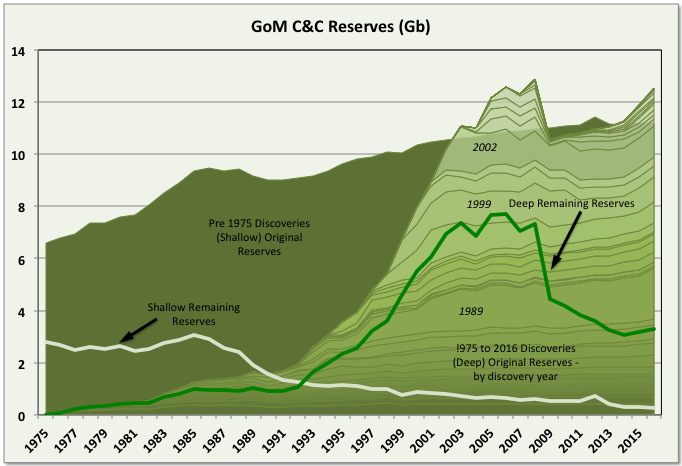
BOEM remaining C&C reserve estimates for GoM increased by 649 mmbbls for 2016 (i.e. to 31st December 2016). This was 112% reserve replacement and followed a similar growth of 618 mmbbls (111% reserve replacement) for 2015. The BOEM reserve calculation method appears to give highly conservative estimates. The increasing reserves followed several years, from 2006, of less than 100% reserve replacement, and actually negative numbers in 2006 and 2008. Current total original reserves (i.e. ultimate recovery) are a new high beating 2006 values, though deep water numbers are still below that year with the main growth appearing to be coming from: 1) older fields that were downgraded because of changes in SPE rules in 2007 (i.e. that reserves could only be booked if there were clear plans for their development within five years); and 2) newer discoveries, mostly smaller fields that are developed through tie-backs to existing hubs. These newer fields often do not get shown as new discoveries because BOEM records production and reserves against leases and each lease is recorded against a single field, even if there are deposits of different depth, age, geology and significant spacial separation within in it.
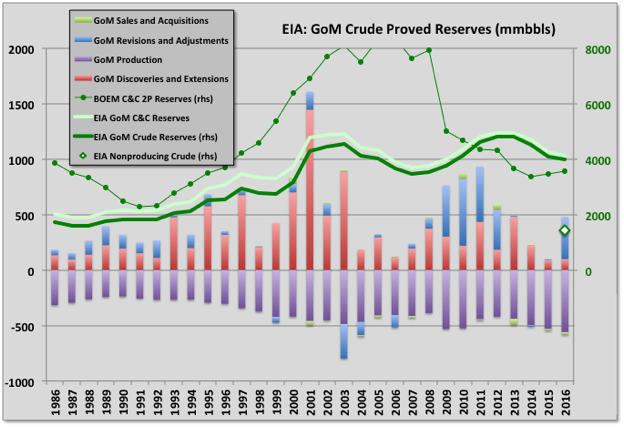
Current oil reserves are 3.569 Gb, which is 15% of the estimated original reserve (aka ultimate recovery). BOEM give the reserves as 2P (i.e. proven and probable) but they look very conservative and are actually lower than the EIA numbers, shown below, given for proven only and based on the operators own numbers, although the two are converging. The historical reserve histories look closer to how 1P (proven) numbers often appear, for example with some fields maintaining near constant R/P numbers, some showing large early drops that then come back over time, and some numbers being suspiciously low on fields obviously not near run out production rates (e.g. Mad Dog and Son of Bluto 2). I think the reserve calculations methods are fairly basic, given the amount of work required they couldn’t be much else, and use volumetric methods (i.e. reservoir area, depth, porosity, recovery factor) and previous decline data (I don’t now if the operators give them additional data such as well pressures).
Reserve Evolution History
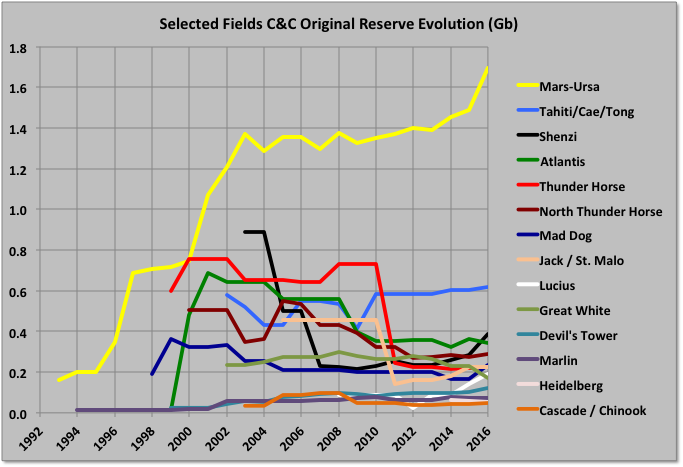
The Mars-Ursa fields have big original reserves, which have shown continuous growth. Other, large deep-water fields have mostly shown negative revisions from original reserve estimates, some quite large, though some of that is due to development timing (e.g. Mad Dog II reserves, when added, will likely recover all the earlier drop, and more). Shenzi has grown recently, and Atlantis will next year, both from new near field discoveries.