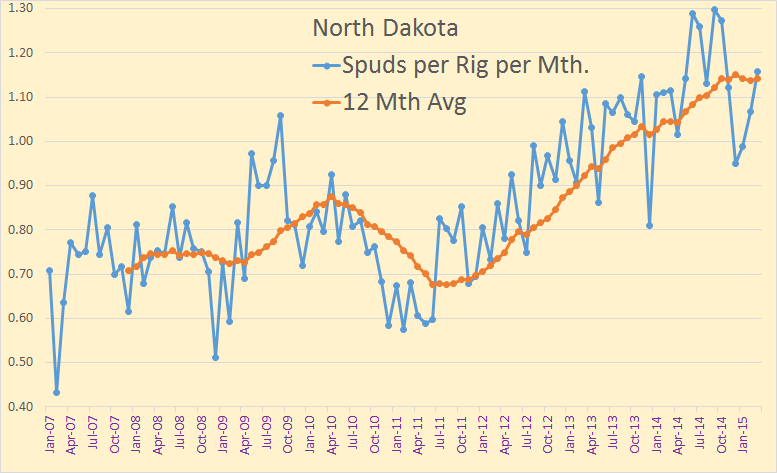
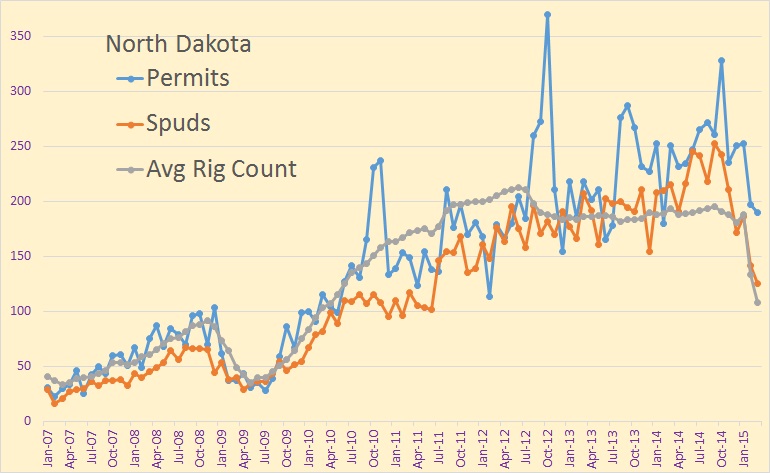
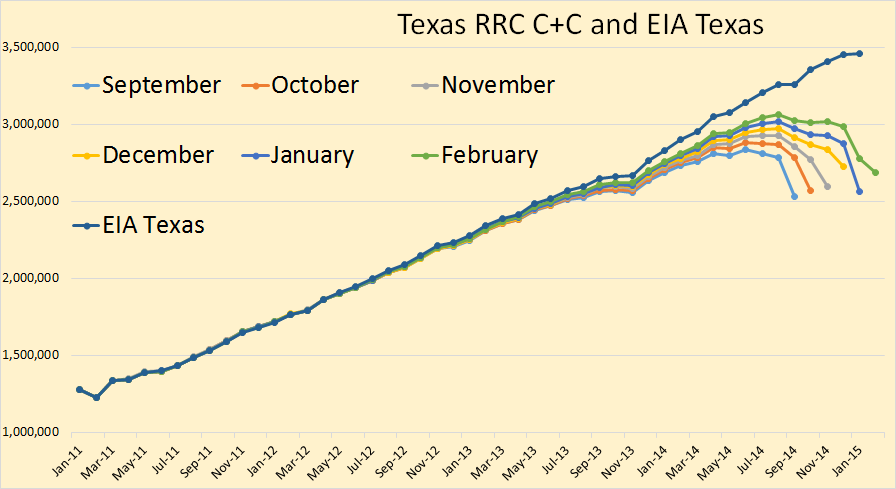
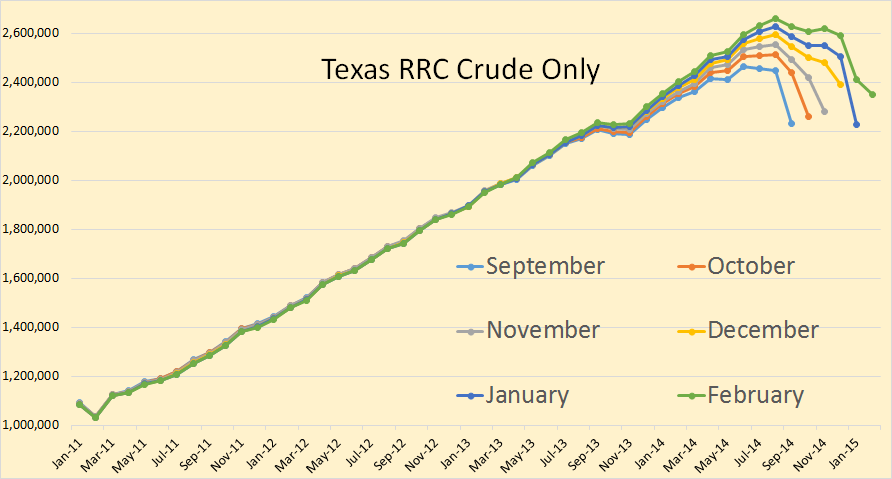
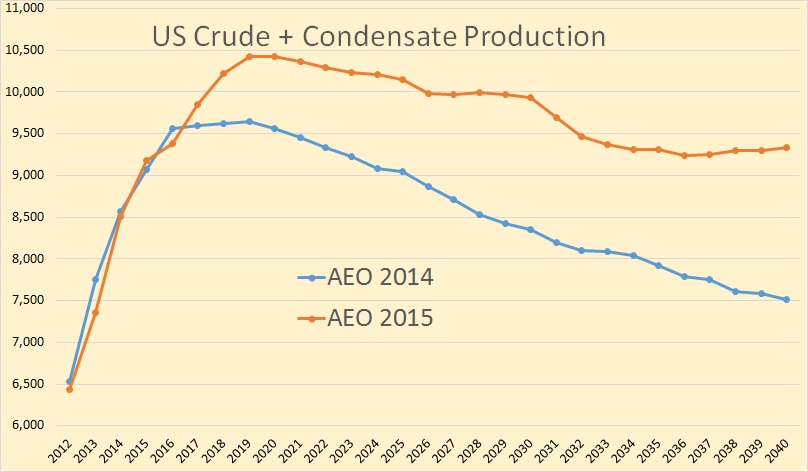
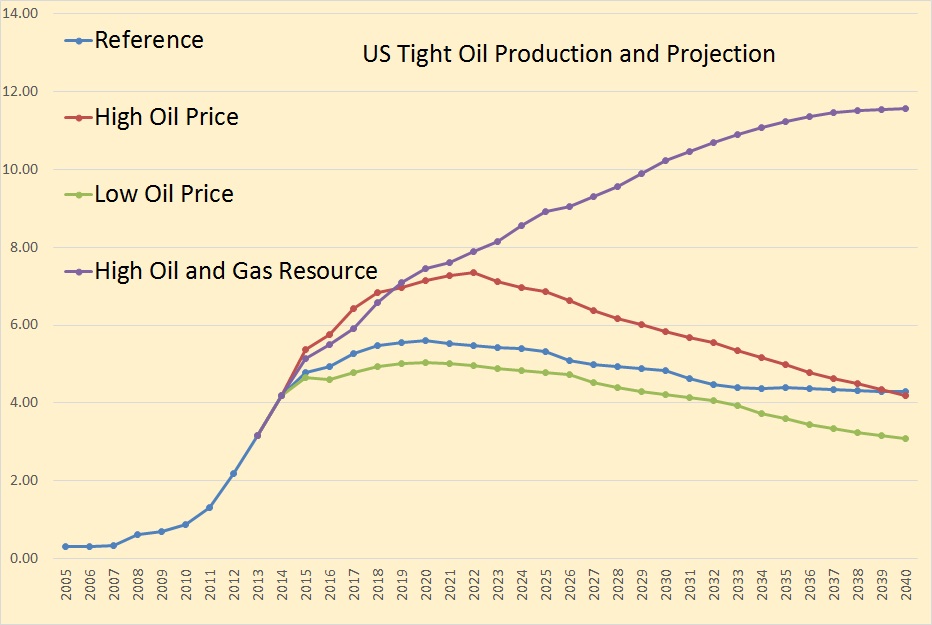
North Dakota publishes, every month, a Monthly Statistical Update from which we can gather a wealth of data if we dig deep enough. They publish the number of spuds, that in new wells started, each month, along with the average number of rigs that month. From this we can glean the average number of days each rigs spends on each well.
The last data point is March, 2015. Through 2011 a rig could drill about .75 wells per month, or about 40 days spud to spud. Today that figure is about 1.14 wells per month or about 26.3 days spud to spud.
Again, the data is through March. We can see the falloff of spuds, rigs and permits in February and March. April and May should show a further decline in all three.