The climate change scientific consensus is summarized via the annual IPCC documents. In one of the IPCC sections, projections of CO2 emissions from fossil fuel usage are made in the context of several scenarios, which are referred to as Representation Concentration Pathways (RCP). Historically, the “business-as-usual” pathway was declared to be RCP8.5.
That has worked out as describing an extreme emission scenario IF society did not take corrective action in reducing emissions. In other words, RCP8.5 tracks a growth path in fossil fuels that is extrapolated from the current economic growth rate and largely dead-reckoned FF production increases.
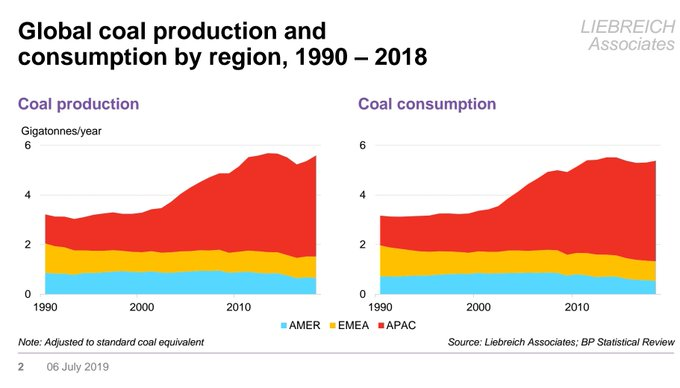
Recently an energy analyst named Michael Liebreich challenged this assumption in the context of the possibility of greater fossil fuel depletion than is currently mapped out in the IPCC, calling the RCP8.5 estimate “bollox” in a tweet. When challenged on this assertion, he rationalized his claim as follows:
“Here’s why I reject scare stories based on RCP 8.5 and SSP5. They assume a vast increase in coal use in the absence of more international cooperation on climate. But the reality is that it coal power is peaking already. Climate change is scary enough, we don’t need ghost stories.”
— Michael Liebreich (@MLiebreich) August 4, 2019