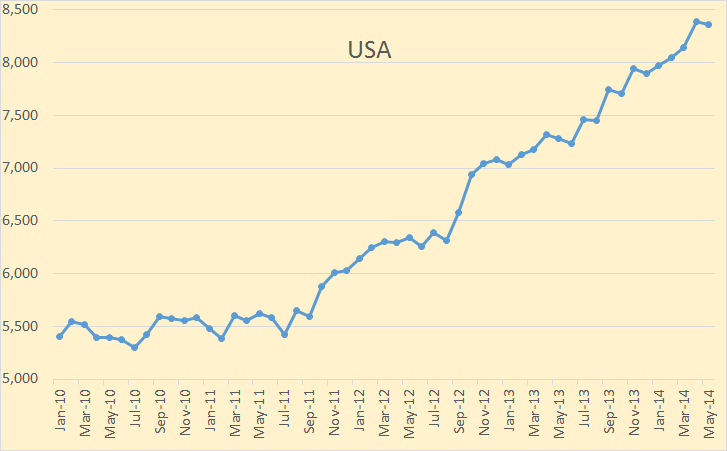
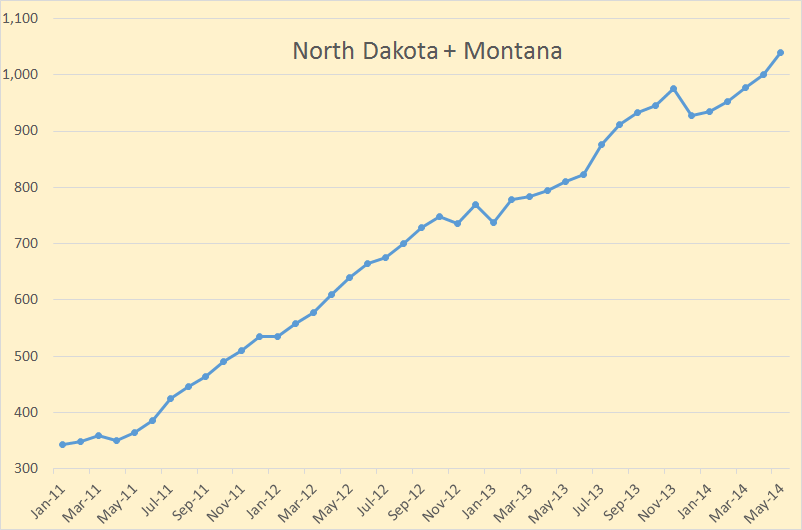
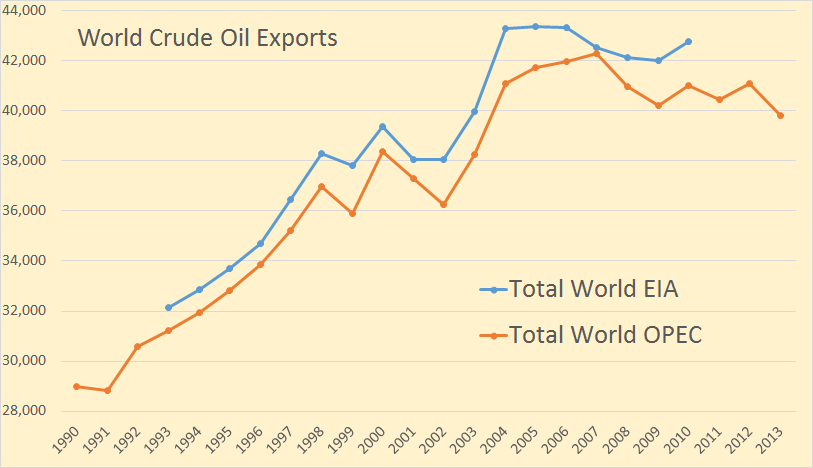
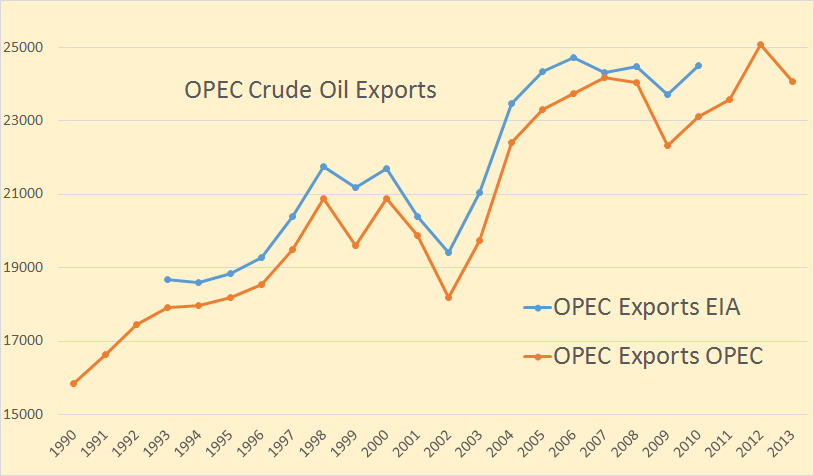
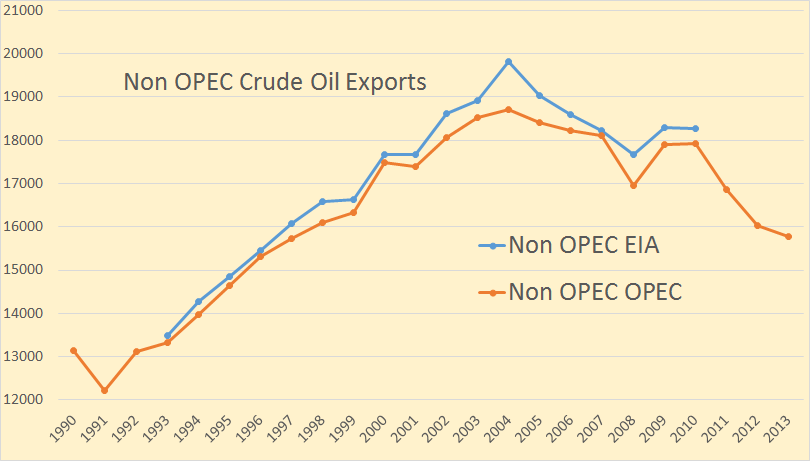
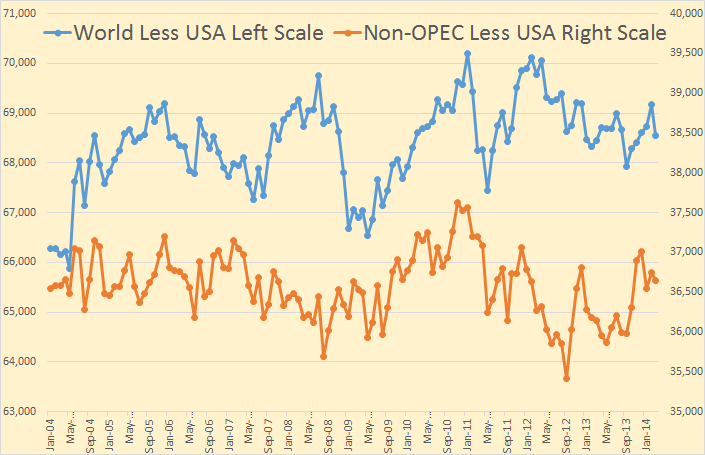
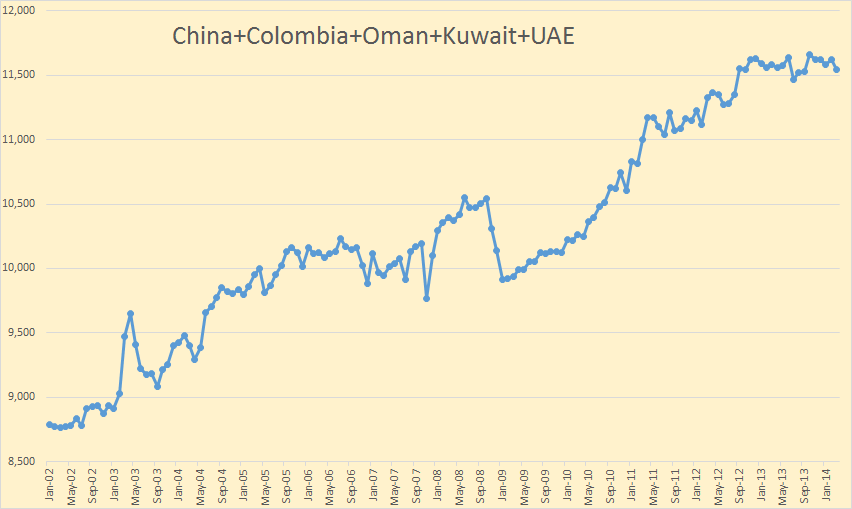
The August OPEC Monthly Oil Market Report is out with the OPEC production numbers for July 2014. There were no big surprises and only small revisions in the June data.
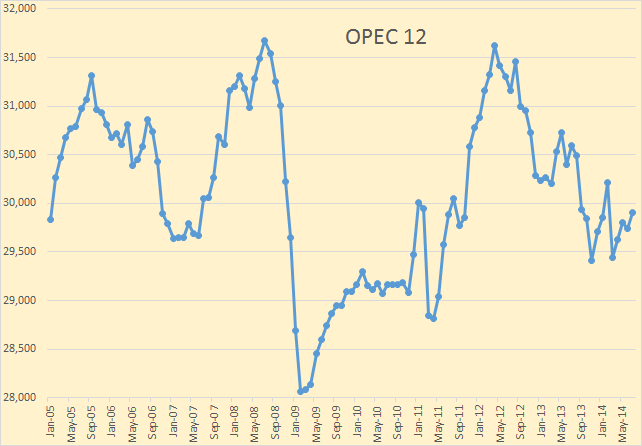
The OPEC 12 was up 166,000 barrels per day. The increase was due to some Libyan oil coming back on line.
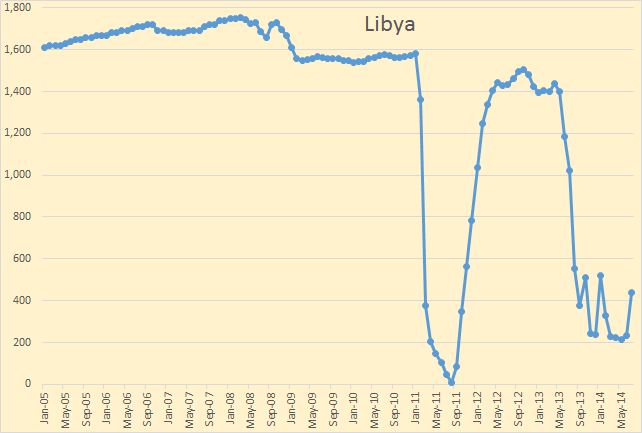
Libyan crude only was up 206 kbd to 438 kbd. Libya was up and down all the month of July and is now down again. From the Wall Street Journal: Risks Remain to Libya’s Oil Supply Despite Reopening of Ports, Fields Behind a pay wall but accessible via Google.
Following an end to protests by a local ethnic group at the country’s largest oil field, called Sharara, Libya’s oil production surged to a five-month high in mid-July to about 600,000 barrels a day—one third of which came from Sharara…
A week after the fighting broke out Libya’s state-owned National Oil Co. acknowledged the country’s output had fallen back by around 100,000 barrels a day.
Read More