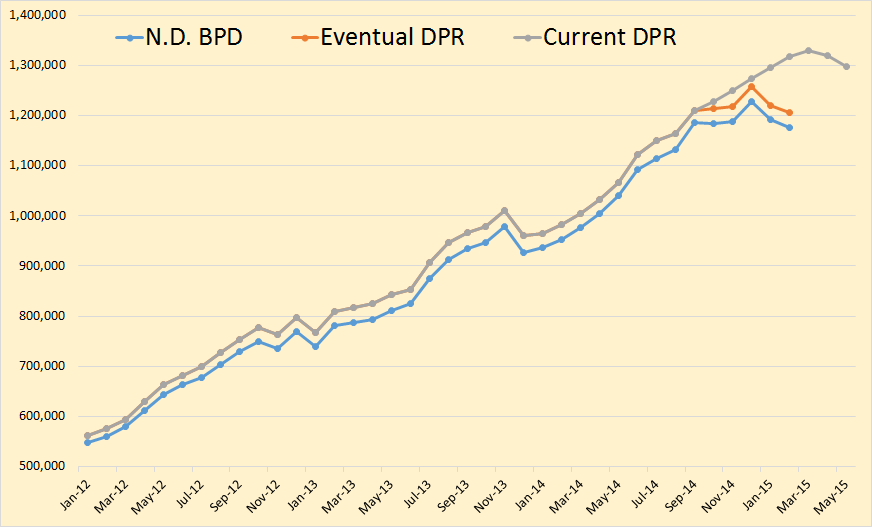
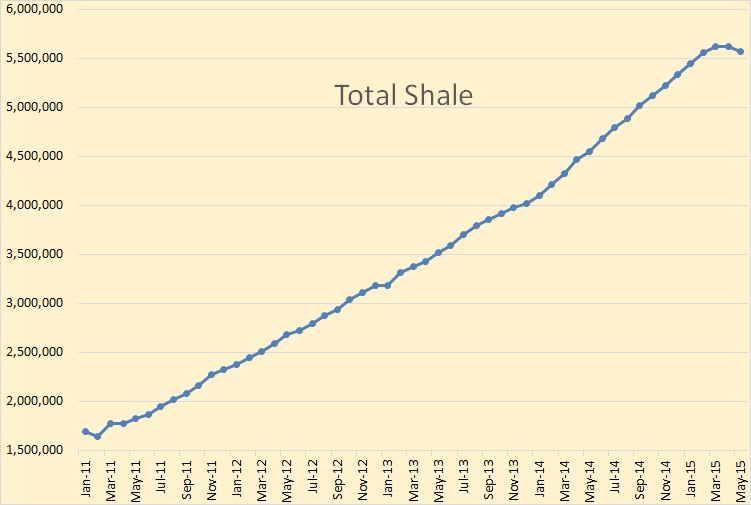
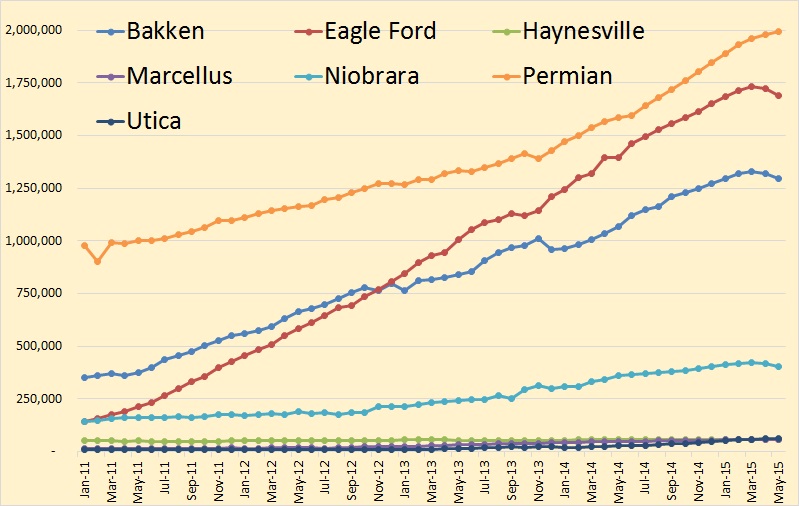
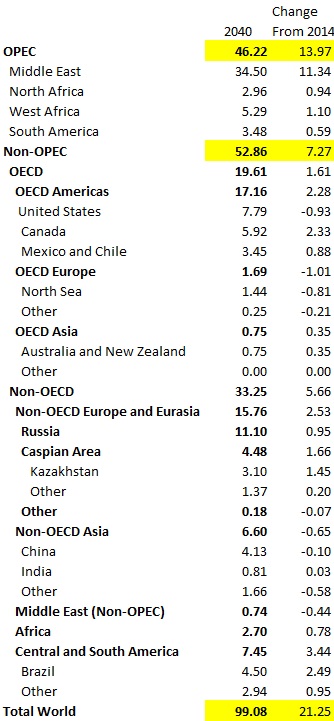
The NDIC Bakken Production Data and the NDIC North Dakota Production Data is in. Production in the Bakken was down 11,941 barrels per day and production in all North Dakota was down 14,104 bpd. The numbers for January were revised slightly. January Bakken was down 35,064 from December and all North Dakota was down 36,331 bpd from December.
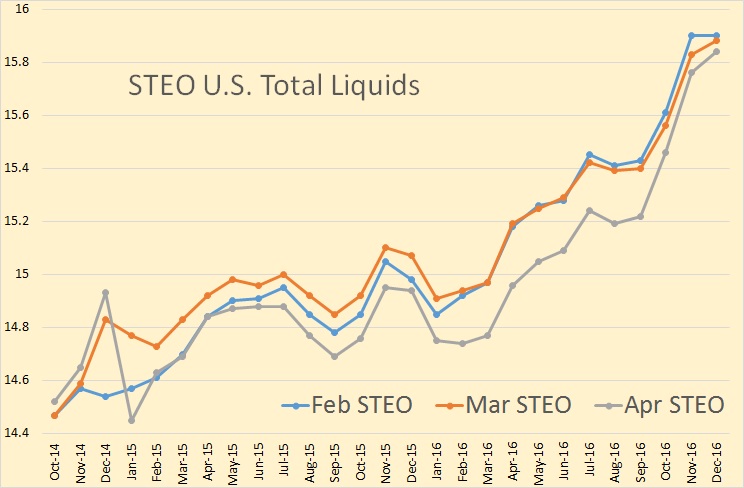
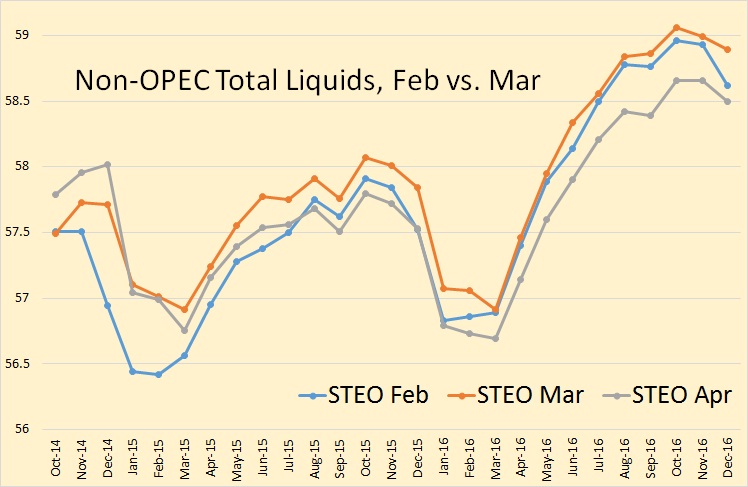
As I have pointed out before, the EIA’s Drilling Productivity Report, for some unknown reason, estimates the last six or seven months, when the actual data is available. In the above chart they estimate from October on. This throws their current numbers way off. The DPR data includes the Montana Bakken therefore their numbers will naturally be higher than the North Dakota data.
Of course the EIA DPR will eventually bring their numbers into what North Dakota is reporting. The above is what the eventual Drilling Productivity Report will look like. (In Orange). Here is the amount the historical DPR is off.