A Guest Post by George Kaplan
Introduction
BOEM produces an estimate of GoM reserves every year. This year’s covers estimates for then end of 2017. Nominally The figures given are 2P estimates but previous analysis has shown them to be extremely conservative, and they strictly follows SEC rules concerning reserves being bookable only if clear development plans are in place.
Backdated Reserves
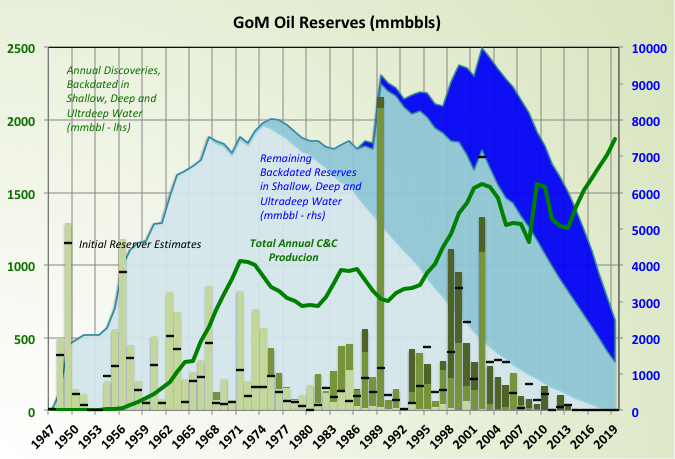
These charts show reserve additions from discoveries by depth (all backdated to the original discovery year so that all adjustments due to improved extraction methods and better understanding of the reservoir etc. are included in the shoen reserve estimate), production and remaining reserves also by water depth.
The black dashes against each discovery show the original estimates of reserves. The shallow water estimates were very low and had significant upgrades, deep water not so much, and ultra-deep hardly at all. The reason for this is mainly the date of the discoveries: nominally it should be easier to apply seismic and drilling analysis from shallow water but the ultra-deep finds were made later and therefore have had better technology and seismic available when the original estimates were made; more on this later.
That said I do not know what method BOEM uses to make the estimates, it cannot be the ultra high fidelity models that the E&P companies use as they do not have the computer power, human resources or time to cover every field in the GoM.