This is a Guest Post By “Political Economist”
In this informal paper, I conduct Hubbert Linearization exercises on the world’s 11 topoil producers as well as the rest of the world. The results are used to project the world oilproduction in the future. The evidence presented in this exercise suggests that the world oil production may peakin 2018 or a few years later.
Hubbert Linearization
Hubbert Linearization (first developed by M. King Hubbert) is a statistical techniqueoften used in the peak oil literature. Hubbert Linearization assumes that oil production rises and falls following a pattern thatcan be described by a logistic function:
Q(t) = URR / [1 + EXP (a(Tpeak-t))]
Q(t) is the cumulative oil production up to year t, URR is the ultimately recoverable oil resources, EXP represents the natural exponential function with the Euler’s number “e” being the base, “a” indicates the intrinsic growth rate of the logistic function, Tpeak is the year of peak oil production, and “t” is the current year.
If one takes the derivative of the above equation with respect to “t”, the above equation can be reduced to: dQ/dt = aQ(1-Q/URR) Replace dQ/dt with P (current annual production) and divide both sides by Q:
P/Q = a – (a/URR) Q
If one uses historical data to conduct a linear regression of P/Q over Q, one can solve the two parameters: “a” and “a/URR”. URR (the ultimately recoverable resources) would be solved accordingly. The peak year could in turn be solved.
If one has historical data, Hubbert Linearization is relatively simple and straightforward. But the method has important limitations. Most importantly, it cannot predict future technical changes that will change the amount of recoverable resources. In many cases, the results of Hubbert Linearization are sensitive to the time period used for regressions. The selection of time period often depends on subjective interpretation of available data.
Nevertheless, Hubbert Linearization does reflect the outcomes of historical interactions of geological, economic, geopolitical, and technical factors as well as their evolving trends. When used carefully in combination with other available information, it can provide useful insights into the future trajectory of world oil production.
The World’s Largest Oil Producers
This paper uses BP’s definition of oil production, which defines “oil” as the sum of crude oil and natural gas liquids. The data are mostly from BP Statistical Review of World Energy, extended to 2013 using EIA’s International Energy Statistics.
By this measure, the world’s eleven largest oil producers in 2013 (ranked by their oil production) were Saudi Arabia, Russia, United States, China, Canada, Iran, Iraq, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Mexico, and Venezuela.
In this paper, all oil production statistics are stated in million tons. For a rough conversion, 50 million tons of annual oil production roughly equals 1 million barrels of daily production.
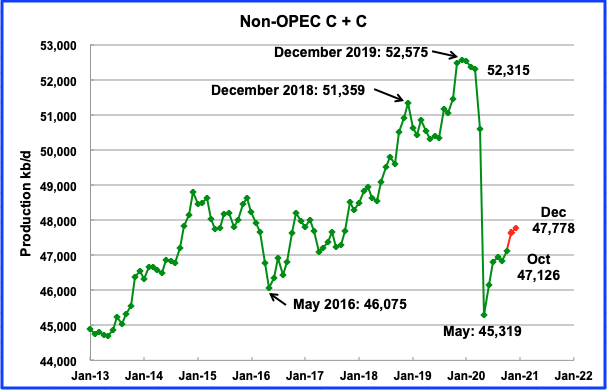
Figure 1

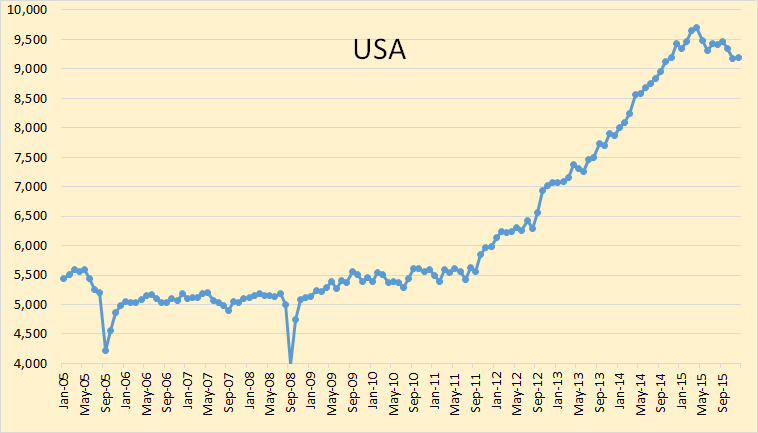
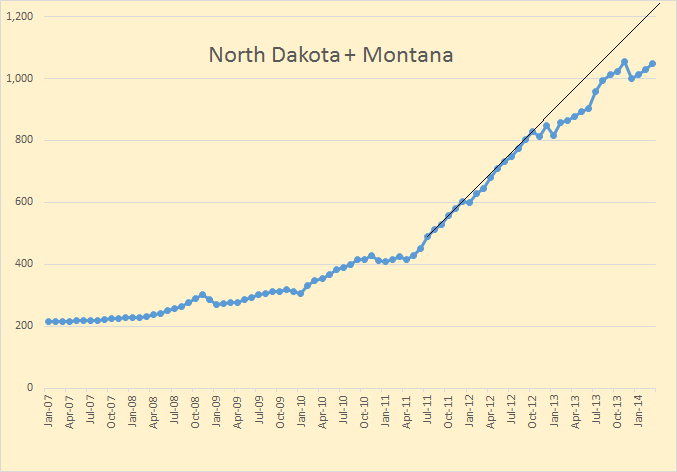
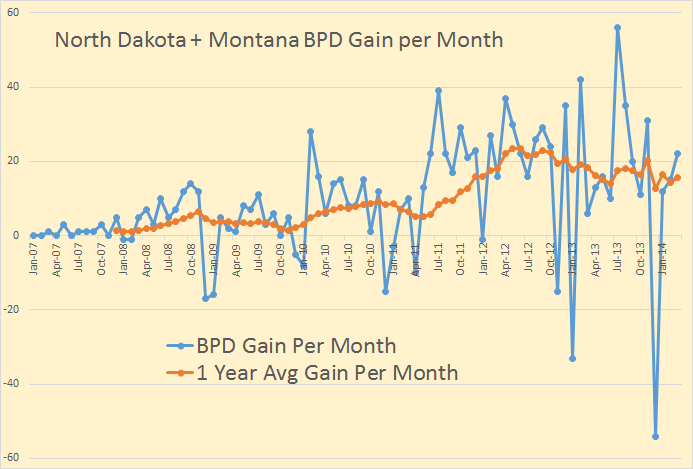
Figure 1 shows the oil production of the eleven top producers as well as the rest of the world. From 2005 to 2013, the world’s total oil production increased by 192 million tons. Saudi Arabia’s oil production increased by 19 million tons, the Russian oil production increased by 57 million tons, the US oil production increased by 139 million tons, China’s oil production increased by 28 million tons, Canada’s oil production increased by 52 million tons, Iran’s oil production fell by 40 million tons, Iraq’s oil production increased by 66 million tons, the UAE oil production increased by 19 million tons, Kuwait’s oil production increased by 23 million tons, the Mexican oil production fell by 44 million tons, Venezuela’s oil production fell by 30 million tons, and the entire rest of the world’s oil production fell by 97 million tons.
Read More